5 min to read
Big Data, Enterprises and Impact
How businesses transcend through Big Data

Big data and business impact is a blog inspired by the learning derived from UCSD (University of California San Diego - Super Computer Center) Big Data Specialization delivered via Coursera.
INTRODUCTION
Data is expected to grow substantially in its volume and veracity over the next years, bringing a raft of opportunities and challenges for businesses across a multitude of sectors. Given that enterprises tactfully embrace the domain, it can provide infinite benefits and room for growth.
In majority context, firms use analytics in the form of summary or descriptive analytics and Business Intelligence (BI) or Management Information (MI) on structured data. And utilize this data in modelling and forecasting procedures.
However, the growing number of challenges businesses face today mean that traditional analytics will be challenged if not obsolete in handling the plethora of data awaiting analysis. As a result, firms will need to review their current status and adapt to these developments or they will lag behind in competition and innovation.

BIG DATA INFRASTRUCTURE, SKILLS AND HADOOP
In order to get going with big data and turn it into insights and business value, it’s likely that the enterprise needs to make investments in the following key infrastructure elements:
- Data storage, organization and processing
- Analytics
- Security
- Languages and proficiency
One stop shop for these infrastructure…
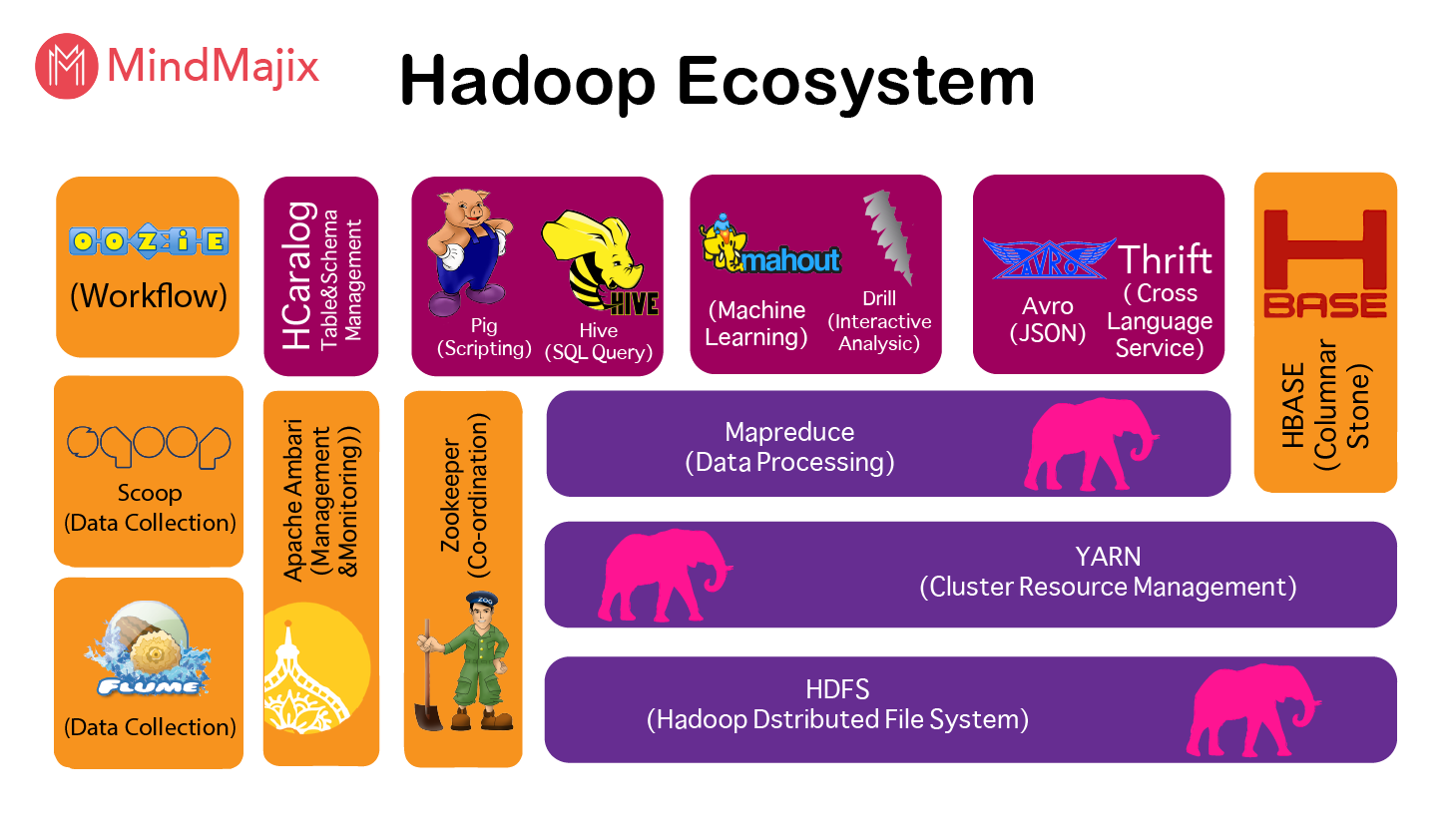
The entire perception of big data and its management went on a revolutionary change with the introduction of Apache Hadoop, an open source Java framework, released in 2010 since the aforementioned key components prevail under the umbrella of hadoop ecosystem at large.
Delving deeper into them and how Hadoop shelter these elements of Big Data is discussed below:
1. Data Processing and Analytics
The collection and organization of raw data to produce meaning and insights for the management is a core achievement of utilizing big data infrastructure. On top of that the mining of data to allow extraction and analysis of data from different perspectives and summation of the findings into actionable insights is of importance, especially on large unstructured data sets collected over a period of time.
Hadoop supports this through the provision of its HDFS or Hadoop Distributed File System, a primary file storage facility that enables easy and quick access to data, irrespective of their volume, across various Hadoop clusters.
While HDFS is the storage part of Apache Hadoop, MapReduce is its processing tool. With MapReduce, it is possible for enterprises to process and generate huge unstructured data sets (remember, each node in the cluster is incorporated with its own storage) across commodity clusters.
This specialization provides the candidates a basic introduction of the eco-system along with a hands-on learning session to establish the conceptual understanding for utilizing clusters for distributed file handling. Furthermore, the course provides the understanding of the impala framework (though in minute detail), which is the primary analytical platform in Hadoop.
2. Security
The Hadoop ecosystem has resources to support security. Knox and Ranger are two important Apache open source projects. Knox provides a framework for managing security and supports security implementations on Hadoop clusters.
The specialization provides no reference as to how this security features work and how the proceeding scalability affects the security concerns of this framework at large. This could be a minor drawback of this specialization in terms of the content provided.
3. Languages and proficiency
While Hadoop is of immense value for the analysis of large volumes of data, the magic happens behind the code the liveware puts into the eco-system of course.
Thus, the main three languages that is essential in handling the hadoop system are as follows:
- Java
JVM (Java Virtual Machine)is the backbone of Hadoop MapReduce. Not only Hadoop, many other Big Data tools are written in Java and they run on JVM. Java is essential for a Hadoop developer who wants to utilize Hadoop code in order to understand the functionality of the system and furthermore to troubleshoot any bottlenecks of the pipeline generated.
- Python
Python has gained a huge popularity as a major language for many trending technologies like Data Science, Machine Learning, AI, Robotics, Big Data etc. Python is simple, open source, general purpose and easy to learn. It has rich set of utilities and libraries which works wonders for Big Data processing. The most common use case of Python in terms of the Big Data domain is the pySpark which provides digestible and comprehensible analytics of large volumes of data in a clustered environment.
- Scala
Scala can be though of as the nemesis of Python and Java in the space of Data Science and is becoming exceedingly popular due to the extensive use of Apache Spark in Big Data Hadoop.
Apache Spark is written in Scala and reputed for Machine learning and streaming Analytics.
The UCSD specialization provides a basic understanding of pySpark, but not of Java or Scala through a hands-on session for the candidates that focus on providing a feel of how the syntax varies from general python in data analytics. The session is comprehensive enough to provide a stepping stone for the aspired candidates to delve deeper into the pySpark space and explore further.
RECOMMENDED IMPROVEMENTS
The course module is well-rounded as an introductory door into the universe of Big Data. For a novel data analyst with a small-scale understanding of big data environment, this course is useful in providing the activation energy for a candidate to explore more and widen the scope of the infrastructure and algorithm used, as it does not reach a greater depth in terms of the Big data eco-system.
Thus, it can be recommended that, inclusion of a more practical savvy assignments which utilizes the cloudera virtual machine and the hadoop infrastructure as a whole, would surely create more value in an industry context for the potential candidates.
4. BIG DATA SUCCESS STORIES
Some of the real life use cases and succes stories of big data and hadoop utilization can be read via the 12 Hadoop case studies in the enterprise thread.


Comments